Exploding Water
Exploding Water
 This experiment demonstrates how a substance can change from a liquid to a gas in an instant! A cup of hot water will immediately explode when a small amount of a very cold alcohol based substance is added. Great care must be taken when performing this experiment, and the cold liquid should be added remotely or from behind a safety screen.
This experiment demonstrates how a substance can change from a liquid to a gas in an instant! A cup of hot water will immediately explode when a small amount of a very cold alcohol based substance is added. Great care must be taken when performing this experiment, and the cold liquid should be added remotely or from behind a safety screen.
As soon as the liquid is added the entire cup of water will explode launching hot water and probably the cup into the air, so it is important to wear safety goggles and to be a good distance away when it happens.
The liquid is an alcohol based aerosol called ‘Tetrafluorethane Dimethyl ether’. The ‘Dimethyl ether‘ part is an organic compound used as propellant in other aerosols and is used with propane for cryogenic freezing.
This substance is found in aerosol cans in DIY or electronics shops but its expensive at around £10. It is commonly used for rapidly cooling electronic parts, removing chewing gum, or for freezing water in pipes that need to be cut. In the shops it can usually be found under the name “Freezer Spray”.
How it’s Done
The freezer spray is designed to evaporate rapidly as it is sprayed onto a surface as this draws heat away from it very quickly. For this experiment the freezer spray must be collected in liquid form before it can be used.
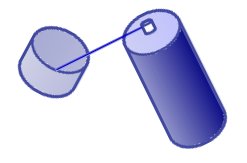 This is done by holding the nozzle in the plastic lid or similar container like shown on the left. The button is then pressed lightly so that the spray starts to come out slowly and collect in the lid. The first bit of liquid will probably evaporate quickly, but as the lid cools down it becomes easier to collect. The amount to collect will depend upon how big the cup of water is and how long it takes to go from collection to adding it to the water.
This is done by holding the nozzle in the plastic lid or similar container like shown on the left. The button is then pressed lightly so that the spray starts to come out slowly and collect in the lid. The first bit of liquid will probably evaporate quickly, but as the lid cools down it becomes easier to collect. The amount to collect will depend upon how big the cup of water is and how long it takes to go from collection to adding it to the water.
Once the liquid is collected it is tipped into a cup of hot water at a distance. It is important that the collected freezer fluid is tipped in at once and not dripped in. If it is added too slowly it will just e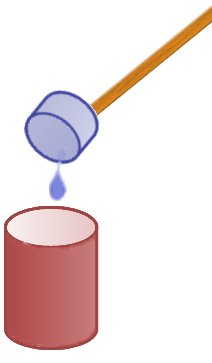 vaporate before any violent reaction can occur.
vaporate before any violent reaction can occur.
Sometimes only fizzing and sputtering occurs, but when done correctly the reaction is immediate and quite powerful.
Important Safety Notes
– The water needs to be hot but not boiling or hot enough to scald.
– The cup holding the hot water should be a light weight plastic type like those from a vending machine.
– The freezer spray should be added to the water away from people, animals, or anything else that would be damaged by hot water.
– The spray should be used outdoors in a well ventilated area away from sources of ignition.
– Safety goggles, gloves and other protective gear are recommended to avoid injury from spilling or

 The reflective film used to make one way windows can react quite violently to high DC voltages. The image on the left shows a piece of window film after being exposed to around 30kV from a low current voltage multiplier.
The reflective film used to make one way windows can react quite violently to high DC voltages. The image on the left shows a piece of window film after being exposed to around 30kV from a low current voltage multiplier.


 These images show how the electrical hot plasma from the Tesla Coil blends with the cold plasma of the flame. Click on the photos for a full view.
These images show how the electrical hot plasma from the Tesla Coil blends with the cold plasma of the flame. Click on the photos for a full view.

 These photos show what happens when pure Neon gas is emitted from the top sphere of a small Tesla Coil. Neon has a much lower ionization voltage than air, so the gas will glow very brightly creating a plasma column to allow the arcs to be much larger. The picture on the right looks similar to the ‘death ray’ devices used in the movie War of the Worlds! You can see when tuned correctly the individual filaments tend to form multiple helices, allowing the plasma column to rise quite high.
These photos show what happens when pure Neon gas is emitted from the top sphere of a small Tesla Coil. Neon has a much lower ionization voltage than air, so the gas will glow very brightly creating a plasma column to allow the arcs to be much larger. The picture on the right looks similar to the ‘death ray’ devices used in the movie War of the Worlds! You can see when tuned correctly the individual filaments tend to form multiple helices, allowing the plasma column to rise quite high.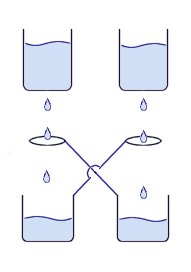 This is a device is a simple method for generating a high voltage charge or static electricity. It works by dripping water through an arrangement of metal containers and loops of wire.
This is a device is a simple method for generating a high voltage charge or static electricity. It works by dripping water through an arrangement of metal containers and loops of wire.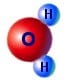 You can see from the image on the right the way that the H2+ is more on one side therefore making an uneven distribution of charge i.e. a dipole. This is what gives water all its interesting properties such as its powerful solvent abilities and its ability to stick to other materials.
You can see from the image on the right the way that the H2+ is more on one side therefore making an uneven distribution of charge i.e. a dipole. This is what gives water all its interesting properties such as its powerful solvent abilities and its ability to stick to other materials.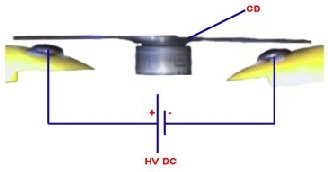 The plastic disc is non conductive, so in order for the charge to get to the other electrode (of opposite polarity), the disk its self must turn. This physical transportation of charge still constitutes a current flow, even though the current does not flow within the material itself. The flowing current is directly proportional to the speed of the rotating disc.
The plastic disc is non conductive, so in order for the charge to get to the other electrode (of opposite polarity), the disk its self must turn. This physical transportation of charge still constitutes a current flow, even though the current does not flow within the material itself. The flowing current is directly proportional to the speed of the rotating disc.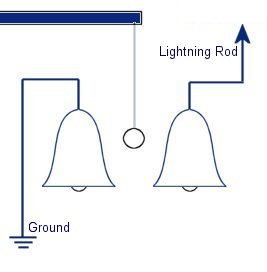 In 1752 Benjamin Franklin was experimenting with one of his inventions, the lightning rod. Using the setup shown on the left Franklin was able collect electrostatic charges from the wind above his house. No known images exist of the original setup used, but this is the most common method used to reproduce the effects he describes.
In 1752 Benjamin Franklin was experimenting with one of his inventions, the lightning rod. Using the setup shown on the left Franklin was able collect electrostatic charges from the wind above his house. No known images exist of the original setup used, but this is the most common method used to reproduce the effects he describes.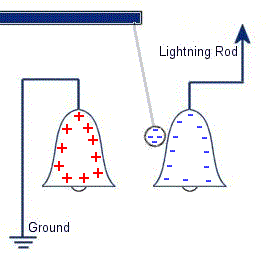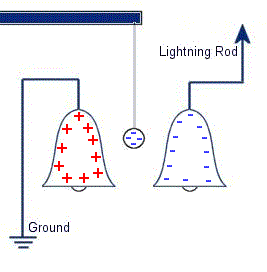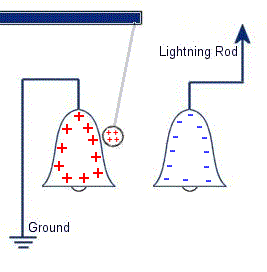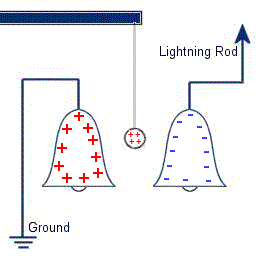 This setup was used by Franklin to collect electric charge for use in other experiments. The amount of charge collected was sometimes so faint that after a spark between the bells it would take considerable time to charge up again. At other times a continuous stream of sparks could be obtained even at lengths of around 20cm.
This setup was used by Franklin to collect electric charge for use in other experiments. The amount of charge collected was sometimes so faint that after a spark between the bells it would take considerable time to charge up again. At other times a continuous stream of sparks could be obtained even at lengths of around 20cm.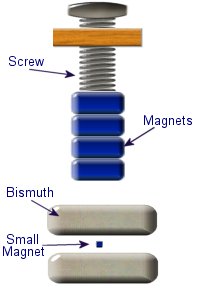 Diamagnetic materials are those that will repel magnetic fields. Many common materials such as water are diamagnetic, but the effect is usually so weak that only super strong magnetic fields will cause any noticeable effect.
Diamagnetic materials are those that will repel magnetic fields. Many common materials such as water are diamagnetic, but the effect is usually so weak that only super strong magnetic fields will cause any noticeable effect.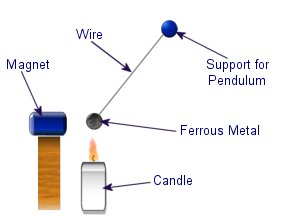 The curie effect usually refers to a magnetic phenomenon discovered by Pierre Curie. He discovered that ferromagnetic substances exhibited a critical temperature transition, above which the substances lost their ferromagnetic behaviour. This is now known as the Curie point.
The curie effect usually refers to a magnetic phenomenon discovered by Pierre Curie. He discovered that ferromagnetic substances exhibited a critical temperature transition, above which the substances lost their ferromagnetic behaviour. This is now known as the Curie point.



